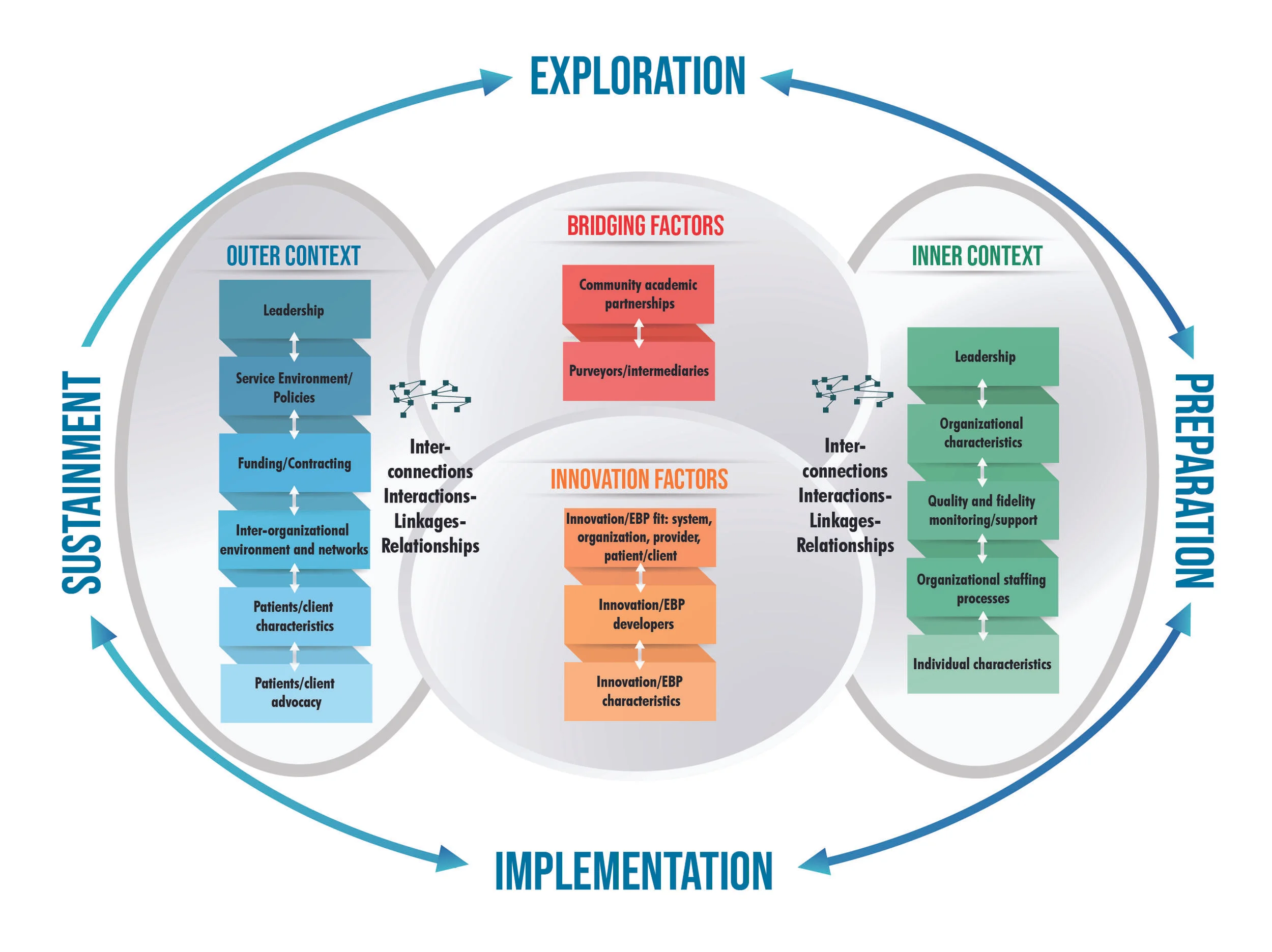
N7303 Translational Science III: Implementation focuses on one of the most critical stages of translational science: putting evidence into practice. While high-quality research is essential, its value is only realised when findings are effectively implemented within real-world settings. This course equips learners with the knowledge and skills required to plan, execute, and evaluate implementation strategies that improve outcomes across healthcare, public health, and organisational systems.
N7303 builds on earlier translational science modules by moving from theory and knowledge generation to practical, sustainable implementation.
Table of Contents
What Is Implementation in Translational Science?
Implementation in translational science refers to the systematic adoption and integration of evidence-based interventions into routine practice. It addresses the gap between what is known and what is actually done in practice.
In N7303, learners examine why evidence-based interventions often fail to scale or sustain and how implementation science can overcome these challenges through structured, context-aware approaches.
Core Learning Objectives of N7303 Translational Science III
By completing N7303 Translational Science III: Implementation, learners typically develop the ability to:
- Analyse barriers and facilitators to implementation
- Apply implementation science frameworks in real-world contexts
- Design and evaluate implementation strategies
- Engage stakeholders to support sustainable change
- Measure implementation outcomes such as adoption, fidelity, and sustainability
These objectives prepare learners to lead evidence-based improvements in complex systems.
Key Implementation Science Frameworks Covered
A major component of N7303 is the application of established implementation science frameworks, which guide how evidence is introduced into practice. Commonly explored frameworks include:
1. Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR)
Used to assess contextual factors such as organisational culture, leadership, and readiness for change.
2. RE-AIM Framework
Focuses on Reach, Effectiveness, Adoption, Implementation, and Maintenance of interventions.
3. Implementation Stages Models
Help learners understand implementation as a phased process rather than a single event.
These frameworks enable learners to design structured, adaptable, and measurable implementation plans.
Identifying Barriers and Facilitators to Implementation
One of the defining features of N7303 Translational Science III is its focus on understanding context. Learners explore common barriers such as:
- Resistance to change
- Limited resources or workforce capacity
- Organisational culture and leadership challenges
- Policy and regulatory constraints
Equally important is identifying facilitators, including stakeholder engagement, leadership support, training, and clear communication strategies.
Stakeholder Engagement and Change Management
Successful implementation depends heavily on people. N7303 emphasises the importance of:
- Involving end-users early in the implementation process
- Building interprofessional collaboration
- Using change management principles to support adoption
- Aligning interventions with organisational priorities
By focusing on human and organisational factors, learners increase the likelihood of long-term success.
Measuring Implementation Outcomes
Unlike traditional research outcomes, implementation science evaluates how well an intervention is implemented, not just whether it works. N7303 introduces learners to key implementation outcomes, including:
- Adoption and uptake
- Fidelity to the intervention design
- Acceptability and feasibility
- Sustainability over time
These measures help practitioners refine interventions and demonstrate value to stakeholders and decision-makers.
Ethics and Equity in Implementation Practice
Ethical and equitable implementation is a central theme in N7303 Translational Science III: Implementation. Learners are encouraged to consider:
- Equity in access to evidence-based interventions
- Cultural responsiveness in implementation design
- Ethical responsibility to reduce harm and unintended consequences
- Inclusive engagement of underserved or marginalised populations
This ensures that implementation efforts promote fairness and improve outcomes for diverse communities.
Assessment Focus in N7303 Translational Science III
Assessments in N7303 are typically application-focused and may include:
- Development of an implementation plan
- Critical analysis of implementation frameworks
- Evaluation of a real or simulated implementation case
- Reflection on leadership and systems-level change
These assessments demonstrate a learner’s ability to translate evidence into practice effectively.
Career Relevance of Implementation Science Skills
The competencies developed in N7303 Translational Science III: Implementation are highly valued across sectors, including:
- Healthcare and clinical leadership
- Quality improvement and patient safety
- Public health and population health programmes
- Health policy and systems management
- Research and implementation science roles
Professionals with implementation expertise play a critical role in ensuring that evidence leads to meaningful and sustained change.
Why N7303 Translational Science III Matters Today
Despite advances in research, many evidence-based interventions fail to reach routine practice. N7303 Translational Science III: Implementation addresses this challenge by preparing learners to:
- Close the research-to-practice gap
- Improve system efficiency and effectiveness
- Support sustainable, evidence-based innovation
- Lead change in complex, real-world environments
Conclusion
N7303 Translational Science III: Implementation is a vital course for professionals committed to turning evidence into action. By combining theory, frameworks, stakeholder engagement, and outcome evaluation, the module equips learners with the practical tools needed to implement and sustain evidence-based interventions.


